Patents
Protection, valorization and transfer of ICIQ’s R&D results
Inventions resulting from the research carried out at the ICIQ that could possibly have commercial or industrial applications are identified and protected as industrial property titles. Subsequently, these are valorized towards a state where they can be licensed to a company or a spin-off. The actions that allow to develop or demonstrate the viability of a technology, from a technical, commercial / economic point of view, are defined, in common agreement with the researchers. The prototype actions and proofs of concept are carried out in the CSOL laboratory.
 At the beginning of 2017, a database has been launched to streamline and make more efficient the management of the ICIQ valorization and technology transfer activities. This database was created by the TTO of the Autonomous University of Barcelona and is being used in other TTOs throughout the country.
At the beginning of 2017, a database has been launched to streamline and make more efficient the management of the ICIQ valorization and technology transfer activities. This database was created by the TTO of the Autonomous University of Barcelona and is being used in other TTOs throughout the country.
During the year 2017, 4 applications for a European patent, one PCT application and a patent application in the United States of America were presented as priority titles. On the other hand, four PCT applications were submitted as international extensions of previous applications. Finally, two patents were granted in Europe.
Similarly to previous years, the La Caixa foundation funded an internal program of grants that has allowed to finance 2 technological development and validation projects aimed at the creation of spin-off companies in the areas of: (i) membranes and materials for the separation of carbon dioxide in gas phase ; (ii) a quantum dots-based diagnostic platform applied to rare diseases. These projects are led by postdoctoral researchers with an entrepreneurial background or mindset and aim at reaching the proof of concept for protected basic research results and facilitating the transfer of the knowledge generated in ICIQ to a spin-off company, designating a entrepreneurial leader of the project. Notably, a total of 5 patent families were transferred in technology transfer operations to 3 different companies, two of which are newly created and one of which counts ICIQ as shareholder (spin-off of the ICIQ).
The following tables summarize research technologies and results protected by intellectual or industrial property rights as of December 31, 2017, the situation of each one of the corresponding intangible assets, as well as relevant vlaorization or technology transfer activities by the year 2017.
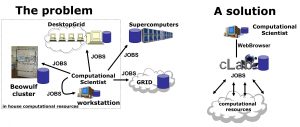
cLab: a web portal to access, use and manage computational resources
The Computational Laboratory Web Manager (cLab) is a web portal that permits the access and the management of a computational laboratory, which is a high performance hypercomputation center based on heterogeneous clusters of computers and used by multiple users simultaneously for the execution of computational jobs. cLab is an internet based application that allows users to manipulate files and folders, prepare computational tasks, submit and control them while they are running, as well as visualize or store results. cLab therefore provide tools for the users as well as for the system administrator.
National Phases:
Europe (EP12704796.7)
United States of America
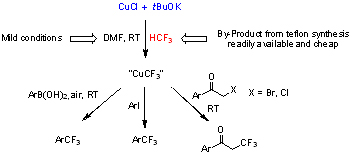
Process to obtain a trifluoromethylating composition
A process for the direct cupration of fluoroform has been developed. This exceedingly simple process employs only cheap reagents and is advantageously run at room temperature to produce CuCF3 reagents that are useful in trifluoromethylation reactions. Chemical compounds bearing a trifluoromethyl group are widely used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals as well as specialty materials, polymers, composites, building blocks, and intermediates for various needs. Fluoroform, CF3H, is an ideal source of CF3 because it is inexpensive, readily available in large industrial quantities, non‐toxic, and not an ozone depleter.
- clean production of trifluoromethyl reagents
- process works at room temperature and atmospheric pressure
- valorization of fluoroform (industrial waste)
- inexpensive and abundant trifluoromethyl source
- low‐cost reagents
US14/401,312
CN104321293
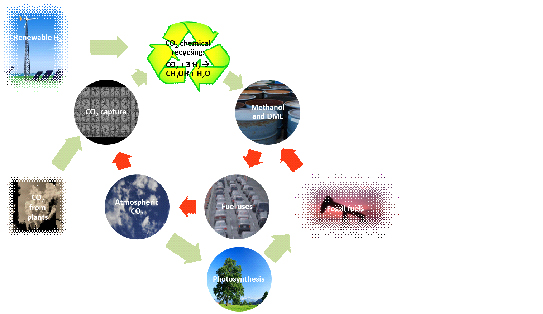
Process for the preparation of methanol and methanol-derived products from carbon oxides
Chemical reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol and its derivatives (such as DME) is considered one of the key technologies to reduce both global warming and fossil fuels dependency. Unlike the currently used process for methanol synthesis, ICIQ’s process provides excellent conversions and selectivity to methanol in one pass through the reactor, thereby providing the highest time yield observed for the chemical reduction of CO2.
- High per-pass conversion
- High selectivity to methanol
- Use of conventional/commercial catalysts
- From CO2 to DME in one sole reactor
- Small reactor size
The Technology has been licensed to the polish company InnoxNova for activities related to demonstration of the Technology in an industrial environament and targeting commercial exploitation of the developed process.
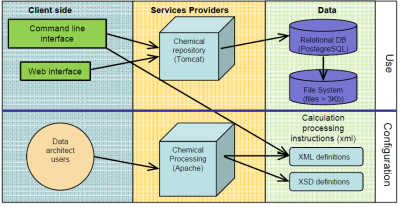
SCIPIO: a comprehensive software interface for computational chemists
SCIPIO is a piece of software that allows to handle, store and manipulate output files from computational chemistry experiments. SCIPIO is a general data extractor and manager that is here presented as a Computational Chemistry Results Repository, which is a sort of tailored electronic notebook allowing for substructure searches and for the generation of “ready to publish” reports.
- Web and Command Line (bash) interface.
- Visualization of chemical structures
- General search & Substructure search
- Automatic generation of “Supporting Information” PDF files for direct publication.
- Calculation and Plotting of “Reaction Energy Profiles” by combining multiple results.
US20160139137
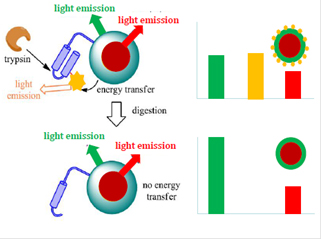
Ratiometric assay for the quantification of hydrolytic enzymes
A nanoparticle containing two different populations of chromophores and funcionalized with a dye-labelled peptide sensitive to the action of a hydrolytic enzyme has been developed. In that way, the optical response of the system can directly be correlated, in a quantitative manner, to the activity of a specific enzyme found in the medium where the nanoparticle is placed, thereby allowing for enzyme quantification. This technology was applied to cystic fibrosis, through the analysis of the trypsin amount of faeces samples. It was shown that this system could allow for the determination of patient’s phenotype, thus avoiding genetic testing.
- non-invasive diagnostic method
- accurate quantification of enzymatic activity
- method can be applied at point-of-care
- fast sample analysis
- Patient phenotype towards cystic fibrosis can be assessed
- Diagnostic platform is versatile
A project targeting clinical validation of the diagnòstic tool was carried out in collaboration with Parc Tauli hospital. This Technology is also the objet of a company incubation project, currently ongoing.
Resistive sensor for the quantification of benzene in the gas phase
Benzene is a volatile and toxic organic compound with strong regulations with respect to exposure. The developed sensor is highly sensitive and selective to benzene, and is based on a specific molecular receptor linked to a carbon nanotube through gold nanoparticles. Benzene recognition by the receptor provokes a bending of the nanotube, which affects the resistivity of the system.
- short response time
- highly sensitive (low levels of detection)
- wearable technology
- no latency between two consecutive measurements.
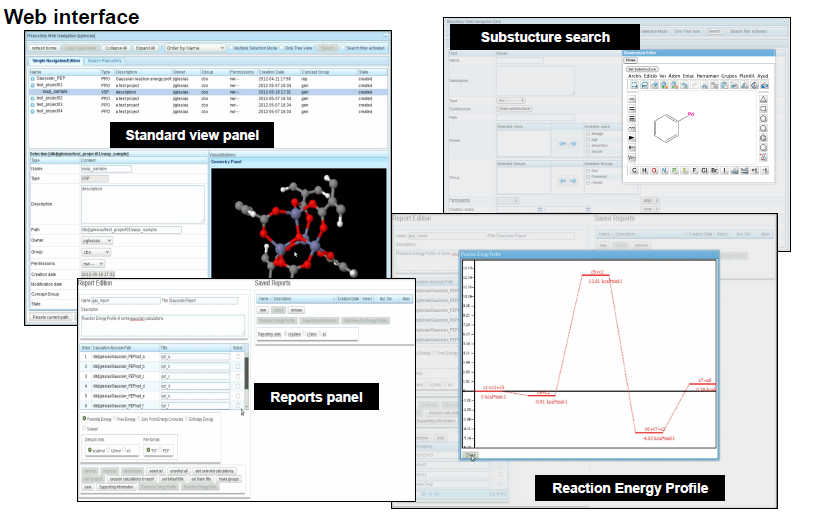
ioChem-BD: a comprehensive software for computational chemists
ioChem-BD is a piece of software allowing for the handling, storage and management of the output files of computational chemistry experiments. ioChem-BD allows for substructure searches and the generation of reports and ready-to-publish materials to make the life of the computational chemist easier.
- Web interface and command line
- Chemical structure visualization
- General and sub-structure search
- Automatic creation of pdf files for ready to publish materials.
- Computation and draw of energetic profiles for chemical reactions.
Software is being distributed to beta-users in the academic sector.
US15/543,151
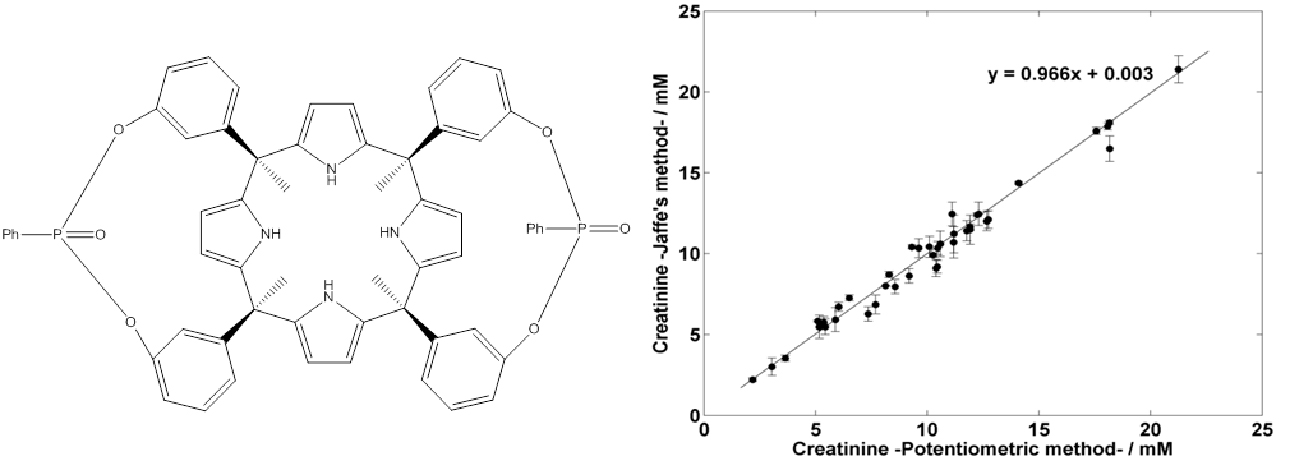
Potentiometric sensor for the quantification of creatinine in biological samples
A potentiometric sensor based on a calix[4]pyrrole receptor specific for creatinine recognition has been developed. The sensor is highly sensitive to creatinine, a biomarker relevant to muscle operation and kidney function. Creatinine quantification in urine samples correlates well with state of the art enzymatic methods (Jaffé).
- short response time
- highly sensitive (low levels of detection)
- wearable technology
- point of care device or potential use in telemedecine
This Technology was transferred to CreatSens Health SL, a spin-off from Rovira i Virgili university constitued in 2017.
EP1671844
US15/564,353
JP554513/2017
Analogs of (-)-Englerin A for the treatment of cancer, diabetes and HIV
New unsaturated analogs of (-)-Englerin A, a natural product highly active for the treatment of renal cancer, have been developed and found to be more active against certain types of cancers than the natural product itself.
- compounds are highly selective for determined types of cancer cells, potentially reducing undesired side effects
- this new family of compounds completes a family of existing drug candidates
This technology has been developed in joint collaboration with the National Cancer Institute (NIH, USA). The technology has been exclusively licensed to NIH for commercial exploitation and licensing to third parties.
Solid sample holder for spectroscopic measurements in cryostats
A sample holder equipped with a circuit of optic fibers and a lens system has been developed, so that it allows the measurement of the spectroscopic properties of solids and other materials when those are placed under controlled environments, such as within a magnetometer or a cryostat.
- cheap solution to bring light to the material and rec-collect and analyze the light passed through the sample
- the device allows studying the optical properties of materials and may unlock new applications for materials
An ERC Proof of Concept, started in fall 2016, is being executed for the prototyping and commercialization of this device. The Technology was transferred to an ICIQ spin-off company, Orchestra Scientific SL, created in December 2017.
Continuous flow preparation of Wieland-Miescher and Hajos-Parrish ktones
A tert-leucine derivative has been successfully anchored onto a polymeric support and shown to be a highly active and selective catalyst for the preparation of the Wieland-Miescher and Hajos-Parrish ketones from readily available starting materials. This catalyst allows for continuous flow preparation of these key building blocks, for the large scale preparation of several natural products and pharmaceutical ingredients.
- catalyst is recyclable and suitable for flow applications
- catalyst is highly selective
- prepared compounds are key intermediates in the preparation of a broad range of fine chemicals, natural products, and pharmaceutical ingredients
Gold-catalyzed preparation of polyacenes
Hydrogenated polyacene compounds are readily prepared in a limited number of synthetic steps using a gold-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization reaction as key synthetic step. The reaction proceeds in mild conditions and exhibits a wide substrate scope. The corresponding unsaturated polyacene compound can be obtained by simple oxidation of the compound. Polyacene compounds are widely used as semi-conductors and as organic electronics.
- New methodology for the fast discovery and development of organic compounds with electronic properties
- Mild conditions and broad functional group tolerance
- Hydrogenated polyacenes are stable precursors of polyacenes
Funding from ERC Proof of Concept project was requested.
Stoichiometric methanol production process
Carbon dioxide is hydrogenated to methanol under high pressure conditions in almost quantitative yields in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of hydrogen. The process is a catalytic heterogeneous process, operating under flow conditions and using a commercial, conventional, methanol synthesis catalyst. Productivity of up to 15 g of methanol per gram of catalyst and per hour can be reached.
- High per-pass conversion
- High selectivity to methanol
- Use of conventional/commercial catalysts
- Stoichiometric amount of hydrogen
- CO2 utilization / circular economy
The Technology has been licensed to the polish company InnoxNova for activities related to demonstration of the Technology in an industrial environament and targeting commercial exploitation of the developed process.
Carboxylation of olefins and alkyl bromides
Olefins and secondary alkyl bromides are carboxylated under mild conditions using a nickel (II) catalyst with a phenanthroline derived ligand. The process goes through a “chain-walking” event, meaning that, regardless the position of the bromine atom or the double bond on the aliphatic chain, CO2 will incorporate in terminal position. This process allows for the preparation of a terminal carboxylic acid from a simple hydrocarbon, using non-selective radical bromination, followed by this regioconvergent process.
- Abundant metal catalyst
- Convergent process: different reactants give one sole product (use of mixtures of starting materials)
- Mild reaction conditions with respect to state of the art processes
- CO2 utilization / circular economy
- Product is easily purified
An ERC Proof of Concept project is being executed to develop and sceren commercial applications of the process, based onthe use of olefins as raw materials.
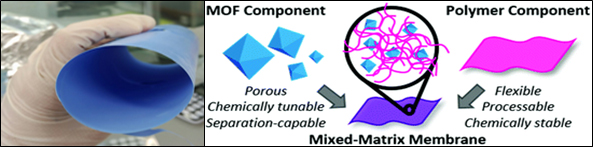
Metal organic frameworks or gas separation applications
A copper (II) based metal organic framework (MOF) is readily prepared from a triazol substituted histidine derivative. The MOF is stable and exhibits good gas absorption properties as well as chirality. The MOF has been proven suitable for CO2 separation, catalysis applications (CO2 hydrogenation, asymmetric catalysis) and chiral resolution. In particular, the MOF offers the possibility to carry out CO2 separation in a continuous manner.
- unique, versatile material
- CO2 separation (e.g. from methane) does not require cycles of absorption/desorption
- Compound can be incorporated into membranes
- Readily accessible material
This Technology is currently the object of a company incubation project and was granted funding from the ERC Proof of Concept grant to be started in 2018. This Technology was transferred to the ICIQ spin-off company Orchestra Scientific, SL, created in December 2017.
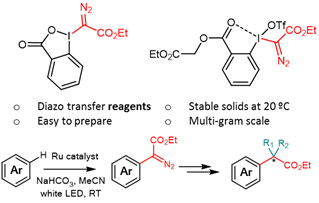
Diasomethylation reagents for carbyne chemistry
The research group of Dr. Marcos García Suero has developed a family of hypervalent iodine compounds able to transfer, when placed under determined photocatalytic ocnditions, a diazomethyl group to aromàtic compounds. These compounds allow the first entry into the chemistry of carbynes and represent a unique method to achieve molecular diversity.
- Possible aplications in late-stage funcitonalization in drug discovery
- Mild condition of reaction and good functional group tolerance
- Stable reagents
- Straightforward further deriviatrization of the introduced diazo group, including halogenation and insertion to C-H,H-O i H-N bonds.
Nickel(0) catalysts
Michigan University is leading the transfer activcities of this Technology.
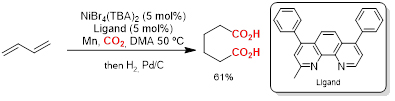
Catalytic carboxylation of 1,3-butadiene and derivatives yielding adipic acids
The research group of Prof. Rubén Martín Romo has developed a catalytic procedure for dicarboxylation of 1,3-butadiene derivatives to form adipic acid derivatives. The procedure is based on the use of nickel as a transition metal responsible for the incorporation of two CO2 molecules into the double bonds of the diene. Adipic acid is a key precursor to the manufacturing of nylon 6,6.
- The current adipic acid preparation method is contaminating and uses a more onerous starting product than the one proposed here.
- The method developed allows adipic acid preparation using CO2 as a reagent.
- The developed method requires fewer synthetic stages than the current method.
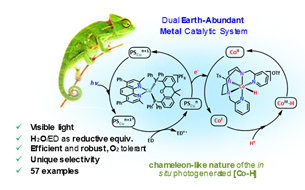
Water-based photocatalytic hydrogenation system
The research group of Prof. Juliol Lloret-Fillol has developed a catalyst system based on cobalt and copper, both abundant metals, and useful in the photocatalytic reduction of C = O (to CH-OH) and C = C (to CH-CH) using water as a source of hydrogen. This catalyst system allows the transfer of hydrogen atoms to organic substrates with very high selectivity and in very gentle conditions, when light radiation is subjected to radiation.
- Unlike other photocatalytic systems, abundant metals are used
- The developed method allows to reduce carbonyl groups in a very selective way
- The reduction process occurs in the presence of water and tolerates the presence of oxygen
- The conditions are smooth and allow to use substrates bearing functional groups.
Temperature-controlled photoreactor device
The research group of Prof. Juliol Lloret-Fillol has developed a photoreactor device to perform parallel experimentation and allwoing irradiation of experimental space with high intensity light, while controlling both the temperature and intensity of light, which provides a very high reproducibility. Unlike commercial devices, the device developed allows to control the temperature of the reactions and avoid overheating of the light sources.
Compounds for treating cancer
In collaboration with the National Institute of Health (USA), the University of Leeds and the University of Delaware, the research group of Prof. Antonio Echavarren Pablos has developed new structures of products derived from the natural product (-) – englerin A, with a high therapeutic potential for the treatment of cancer
- Compounds are highly active and selective in inhibiting the growth of certain tumoral cell ines, resulting in a decrease of undesired secondary effects.
New family of compounds which complete the library of (-)-Englerin A analogs reported previously
Photocatlytic method and catalyst for the ether functionalization
The research group of Prof. Rubén Martín Romo has developed a photocatalytic process of functionalization of ethers. The reaction does not require the use of photosensitizers or species based on rare transition metals, but uses a photocatalytic system that consists in the combination of a complex of nickel and a diarylketone used in irradiation with visible light.
- Mild reaction conditions
- Method applicable in the presence of functional groups
- Possible applications in late-stage functionalization
- Commercial components
The following table summarizes the main indicators related to the activities of protection and transfer of the R&D results of the ICIQ for the year 2017:
| Patent applications per country | granted patents per country |
Transferred patents per country |
Signed Transfer agreements |
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | US | PCT | FR | GB | DE | JP | CA | AU | CN | US | CN | ES | GB | DE | FR | EP | PCT | US | CN | 4 |
| 11 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |
Finally, in order to promote entrepreneurship and disseminate best practices in the valorization and transfer of technology among the ICIQ research staff, in 2017 a training program has been carried out, based on the following three actions :
- Description of the operation and the mechanisms of management of the industrial and intellectual property of the ICIQ - Training of 2 hours directed to all the researchers of the Institute (25-30 attendees).
- Practical aspects of the valorization of the results of the research - Training of 4 hours duration, with 30 attendees and given by Arvor Consulting.
- From Science to Business - Training of 3 days, directed to a selected group of 5 ICIQ researchers with spin-offs business creation projects, delivered by the ESADE business school and organized by Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (BIST). The objective was to detail the mechanisms of management of innovation and scientific entrepreneurship.